At Nested Knowledge, we are committed to transparency and rigorous evaluation of our AI-powered review tools. This page compiles validation studies across the core stages of the evidence synthesis workflow: Search, Screening, Data Extraction.
For each stage, we provide internal assessments and external, third-party evaluations, including academic reviews, NICE compliance alignment, and independent comparative analyses. These studies demonstrate both the feature evolution of our platform and the real-world performance of our tools in clinical and regulatory research contexts. This page is to provide evidence of the reliability, accuracy, and proper functioning of the AI tools embedded in Nested Knowledge (NK).
Notably, recent external benchmarking placed Nested Knowledge as outperforming three other automation platforms. See the linked abstract and poster in Tool Reviews and Feature Comparisons for full details.
1. Overview and Critical Links #
- Published Overview of Methods and AI Validations (July 2025) – this publication details a complete methodology for utilizing our AI SLR tool with human-in-the-loop curation workflows, as well as AI validations, time savings, and approaches to ensure compliance with best review practices.
- Citation: K. M. Kallmes, J. Thurnham, M. Sauca, R. Tarchand, K. R. Kallmes, and K. J. Holub, “ Human-in-the-Loop Artificial Intelligence System for Systematic Literature Review: Methods and Validations for the AutoLit Review Software,” Cochrane Evidence Synthesis and Methods 3 (2025): 1-13, https://doi.org/10.1002/cesm.70059.
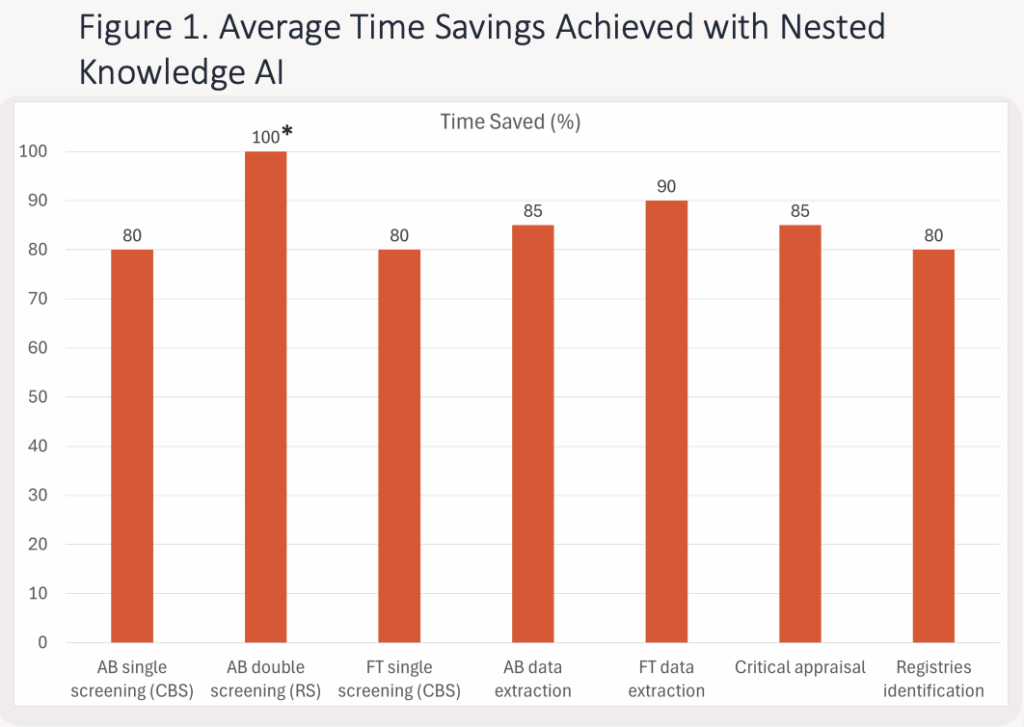
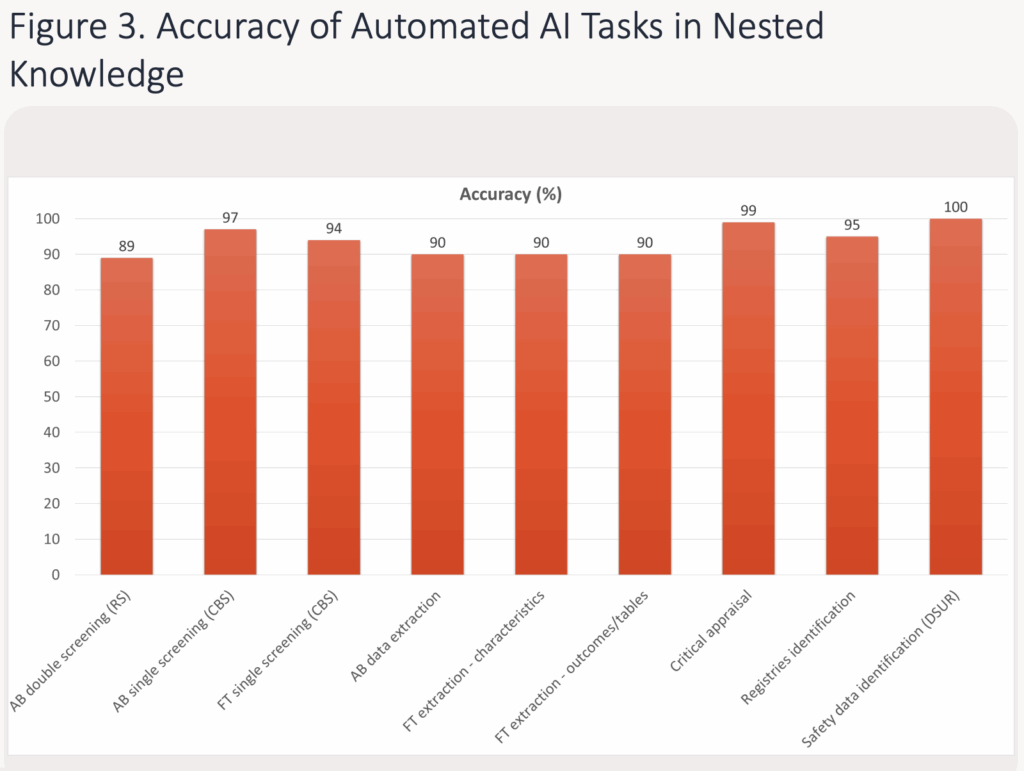
- External Validation Assessment and Publication of Nested Knowledge AI Tools (Nov 2025) – this independent evaluation assessed the performance of AI tools in AutoLit across the full literature review workflow, including Smart Search, Robot Screener, Adaptive Smart Tags for data extraction, and automated critical appraisal. Across multiple real-world projects, each AI capability achieved ~85% time savings and 90%+ recall, with some functions surpassing human reviewers in accuracy. The study highlights how recent AI advances are already transforming evidence synthesis, even as the field continues to evolve. See accompanying poster presentation.
- AI in Nested Knowledge – how AI powers our platform
- NICE Compliance Guide – how Nested Knowledge aligns with UK standards for clinical evidence
- Use Cases and Case Studies – real-world applications across all domains in the evidence synthesis life-cycle
2. Validation Studies by Workflow Stage #
Literature Search #
- Smart Search is a human-in-the-loop reasoning agent in Nested Knowledge that uses LLM-driven chain-of-thought logic to build Boolean search strings after input of a research question, achieving over 75% recall in validation against Cochrane and in-system SLRs. The tool significantly outperforming black-box LLM approaches. See published ISPOR USA 2025 Abstract and accompanying presentation.
Screening #
- Robot Screener is a machine learning-based AI tool in Nested Knowledge that replaces the second reviewer in a Dual Screening workflow. The tool prioritises high recall to ensure no relevant studies are missed during abstract screening, achieving up to 97% recall in internal studies and comparable performance to human reviewers in external HEOR-focused validations. This makes Robot Screener a powerful, time-saving asset for high-quality, comprehensive SLRs and HTAs.
- See published ISPOR USA 2024 Abstract (internal) and accompanying poster presentation.
- See published ISPOR USA 2024 Abstract (external) and accompanying poster presentation.
- View summary of validation statistics and explanation of how the statistics work.
- AI Time and Motion – Analysis of the Accuracy and Efficiency of AI for HTA-Standard SLRs – In a dataset of 234 studies, hybrid-AI screening delivered the best balance of performance (97% accuracy) with a 51% time reduction, while fully-AI screening delivered the largest efficiency gains (81% time savings) but lower recall. For data extraction, fully-AI extraction reached 95.7% accuracy and cut extraction time by 93%. Overall, the study demonstrates that AI, especially hybrid approaches, can substantially accelerate evidence generation with accuracy comparable to or better than manual review. (ISPOR EU 2025 Abstract)
- AI-Assisted Screening in Targeted Literature Reviews (TLRs) – This study evaluated the performance of Robot Screener across five diverse TLRs. Using a model trained on known citations, the tool prioritised abstracts with high relevance scores, reducing the screening workload by ~90% while maintaining strong performance (recall 0.88–0.97). Fewer than 10% of abstracts required human review, yet all research questions were fully addressed. The findings demonstrate that Robot Screener provides highly efficient, conservative prioritisation with 90%+ recall, supporting rapid and reliable evidence identification across varied review contexts. (ISPOR EU 2025 Abstract)
- Use in Oncology-Focused TLRs –
Tagging (Data Extraction) #
- Core Smart Tags (CSTs) are a specialised AI tool in Nested Knowledge that combine machine learning, NLP, and heuristics to extract and hierarchically structure key clinical data from a research question. This includes extracting PICOs, study type, location, and size with validated accuracy and human-in-the-loop oversight, enabling faster, reliable evidence extraction for clinical SLRs.
- See published ISPOR USA 2025 Abstract and accompanying poster.
- PICO Prediction for Joint Clinical Assessments (JCA) — This study used Nested Knowledge to map and consolidate PICOs for Soft Tissue Sarcoma (STS) ahead of JCA, revealing extensive heterogeneity, dozens of country-specific PICOs and divergent treatment patterns and demonstrating how structured AI-supported searching can streamline PICO assessment for complex conditions. (ISPOR EU 2025 Abstract)
- Adaptive Smart Tags (ASTs) leverages AI to automatically highlight and extract user-defined variables across abstracts and full texts, achieving up to 80% match to manual extraction in validation studies enabling faster, intuitive and audit-tracked data structuring for complex clinical reviews.
- Version 1: See published GES Prague 2024 Abstract and accompanying poster.
- Version 2: See unpublished, internally conducted online statistics.
- Assessing Accuracy of Data Extraction of GLP-1 Agonists for Weight Loss — This study validated Nested Knowledge’s unsupervised Adaptive Smart Tags, showing exceptionally high accuracy (F1 ≈ 0.98) in identifying key concepts across GLP-1 RA RCT abstracts, demonstrating that LLM-driven tagging can reliably support faster, higher-quality screening and early data extraction.
Meta-Analytical Extraction #
- Smart Meta-Analytical Extraction (SMAE) is an AI tool that generates a rapid meta-analytical outputs, such as forest plots, from chosen studies and their accompanying full texts.
- Released May 2025, it is currently in beta.
- AI-assisted Quantitative Extraction of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) — This study evaluated Nested Knowledge’s AI-assisted data extraction in ALL studies, showing ~95% time savings and accurate AI-generated summaries, while highlighting the need for human review to address incomplete extractions—especially for heterogeneously reported outcomes. (ISPOR EU 2025 Abstract)
3. Tool Reviews and Feature Comparisons #
- Feature Comparisons Table
- Function-by-function match-up across systems conducted by Nested Knowledge prior to feature-completeness
- Updated in 2023
- External Reviews of entire tool
- For academic research
- For clinical reviews in regulatory research: Abstract and Full Text
- Living evidence map: position of NK in automation ecosystem
- Nested Knowledge vs three other systems
- Nested Knowledge was concluded as the most comprehensive, effective tool referred to by “T1”. See published ISPOR USA 2025 Abstract and accompanying poster presentation.
Do you have further questions about how our AI tools work? Let us know!

