There are several tools in Nested Knowledge that utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to make systematic reviews easier and more effective to conduct. This page provides technical details on what these features are, and how your data is used.
1. RoboPICO #
- Used to highlight Populations, Interventions/Comparators, and Outcomes in abstracts during Screening
- Optional: by default this feature is toggled on, but can be toggled off and will remain off for all abstracts in the queue/ongoing modules and Study Inspector until toggled back on.
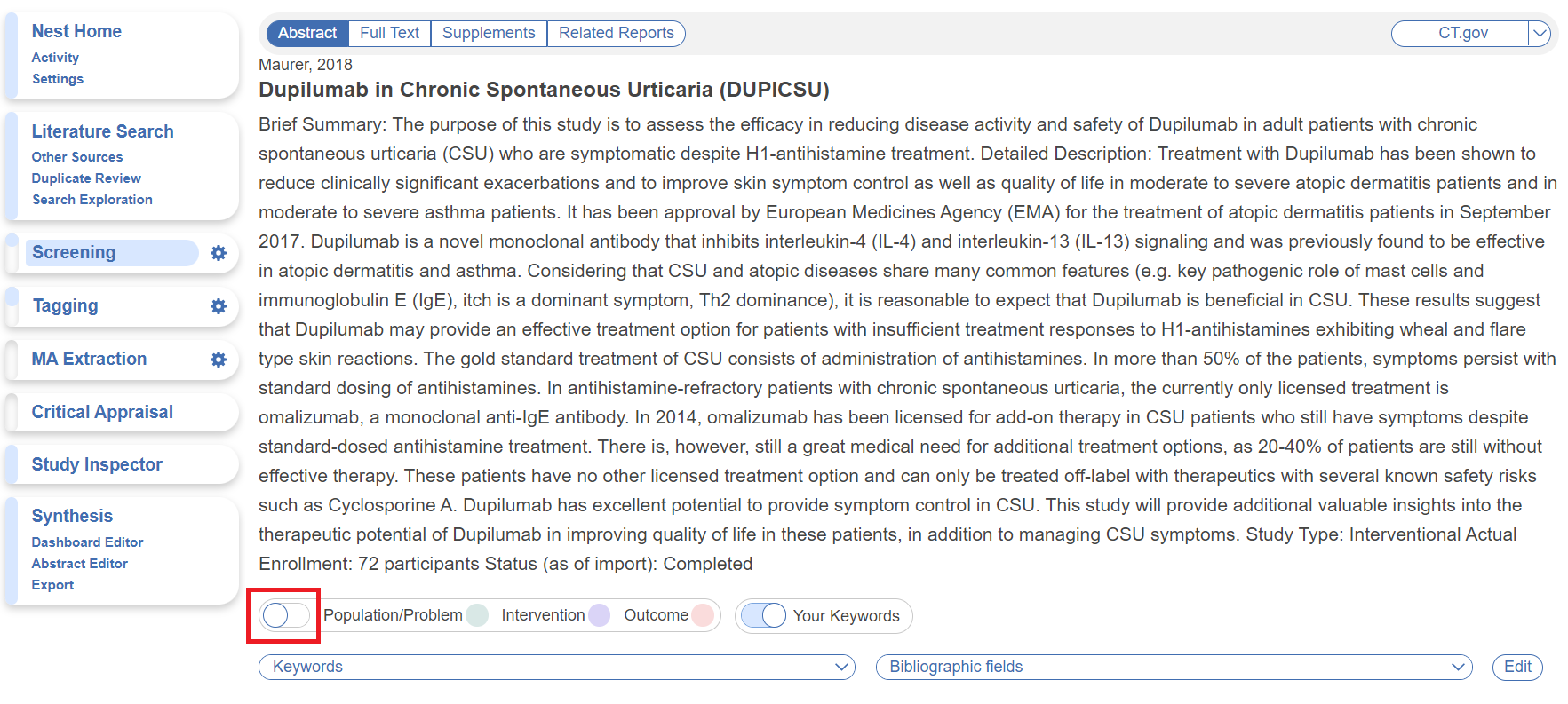
- Optional: by default this feature is toggled on, but can be toggled off and will remain off for all abstracts in the queue/ongoing modules and Study Inspector until toggled back on.
- Used to generate most commonly reported terms among the literature, to inform the build of search queries in Search Exploration
- Optional: Search Exploration is not a required step in AutoLit and simply offers assistance to build a search. However, when it is used, RoboPICO auto-generates terms when concepts are entered and “Refresh Exploration” is selected. This cannot be switched off when Search Exploration is used.
a. Which data does RoboPICO use? #
The abstract of records is made available to the model.
b. How does the model work? #
RoboPICO uses a fork of the machine learning system offered by RobotReviewer. Specifically, Named-entity Recognition models extract Patient/Problem, Intervention, and Outcome entities from data in article abstracts. NK’s modifications to RobotReviewer are open and General Public Licensed.
This model is not trained or updated from your data.
2. Smart Search #
Smart Search prompts user input of a research question, encourages refining of said question, and generates varying-sized corresponding search strings for use in searching PubMed.
a. Which data does Smart Search use? #
Smart Search uses only the text inputted into the research question and, where applicable, responses to prompts used to refine the research question.
b. How does the model work? #
Smart Search is a an agent-based LLM system that employs an iterative generator-critic loop to generate and assess Boolean strings based on user-entered textual Research Questions and iterative chat-based user clarifications. See our full model card for Smart Search, which also uses Research Question refinement.
This model is not trained or updated from your data.
3. Bibliomine #
Bibliomine extracts references from full text PDFs. Typically, previous systematic reviews or landmark studies are bibliomined, importing all cited references as records directly into your nest. This feature does not access your data unless you use it.
Optional: This feature is helpful if, for example, you are performing an update on an existing review, but is not required to successfully upload records to a nest.
a. Which data does Bibliomine use? #
Bibliomine consumes any PDFs uploaded for its purposes. It writes records with full bibliographic data to your nest (pending user addition).
b. How does the model work? #
Bibliomine uses Cermine, an open source machine learning library for mining documents. Using DOI & title extracted, full bibliographic data will be retrieved from PubMed or CrossRef (in that order of preference).
This model is not trained or updated from your data.
4. Robot Screener #
Robot Screener uses a model trained on human screening decisions to make reviewer-level screening decisions based on inclusion probabilities. In effect, it replaces one human reviewer when turned on in nests with a Dual Screening mode. This feature does not have access to your data unless you turn it on in Settings.
Optional: This feature is helpful to speed up the Screening process, but is not required to successfully Dual Screen all records in a nest.
a. Which data does Robot Screener use? #
The following data from your records are model inputs:
- Bibliographic data
- Time since publication of the record
- Page count
- Keywords/Descriptors
- Abstract Content
- N-grams
- OpenAI text embedding (ada-002)
- Citation Counts from Scite, accessed using the DOI
- Number of citing publications
- Number of supporting citation statements
- Number of contrasting citation statements
The model is trained on adjudicated AB or FT screening decisions, depending on your screening mode. This includes the exclusion reason. Similarly, the model outputs a screening decision for each record requiring a reviewer-level decision.
If enabled, Robot Screener will continuously screen new records as they imported into your nest.
b. How does this model work? #
Learn more about the screening model that generates inclusion/advancement probabilities for Robot Screener. A probability threshold, optimized on a geometric mean of precision and recall in a cross validation, determines if records should be included or excluded.
This model is only available within your nest & its parameters are not shared with other nests or users.
5. Criteria-Based Screening: Smart Screener #
Criteria-Based Screening (CBS) allows users to input their inclusion criteria via yes/no questions and Smart Screener answers these questions using the study Abstract and/or Full Text, attaching an annotation. Users are encouraged to review these answers before manually assigning a screening decision, but may bypass this by applying a threshold of criteria met in order to include/exclude studies in bulk.
a. Which data does Smart Screener use? #
Answers are generated for abstracts or full-text PDFs at the user’s discretion. You instruct the model through:
- Criteria Name
- Question Contents
b. How does the model work? #
Smart Screener uses an OpenAI LLM to identify relevant concepts or answer questions about plain-text reductions of abstracts and full-text PDFs. The model’s recommendations relate to the Abstract/PDF as an annotation using fuzzy (edit distance) search.
The model, and OpenAI in general, is not trained or updated using your data.
6. Core Smart Tags #
Core Smart Tags (CSTs) prompts user input of a research question, encourages refining of said question, and builds a tag hierarchy/data extraction template of PICOs, Study Type, Study Location and Study Size based on all study abstracts. It also extracts this data for review.
a. Which data does Core Smart Tags use? #
Core Smart Tags uses each study’s title, abstract and bibliographic data to determine the appropriate categorization and extraction of the given concepts.
b. How does this model work? #
Core Smart Tags (CST) is an integrated system for extracting, analyzing, and structuring information from biomedical research abstracts. It combines independent models and tools to generate a comprehensive overview of study characteristics. The CST system includes:
Hierarchy Tool: Generates a hierarchical structure of entities based on PICO extractions to allow users to navigate studies by specific attributes (e.g., interventions > vascular surgeries > thrombectomies).
Smart Sample Size (SSS): Extracts the sample size from abstracts with a heuristic-based algorithm.
Smart Study Location (SSL): Identifies the geographic location of studies by extracting references to countries and cities.
Smart Study Type (SST): Classifies abstracts into predefined study types (e.g., clinical, cohort, observational).
BioELECTRA-PICO: Extracts PICO (Participants, Interventions, Outcomes) elements using a fine-tuned transformer model.
Additionally, research question refinement is used.
This model is not trained or updated from your data.
7. Adaptive Smart Tags #
Adaptive Smart Tags (ASTs) are context-aware recommendations of relevant concepts in study abstracts and/or full texts using an OpenAI Large Language Model (LLM). These recommendations include provenance via an annotation within the abstract or PDF, making review of the model’s work possible. It also provides the option to bypass this review and auto-extract relevant data for rapid exports.
Optional: This feature is helpful to speed up the data extraction process, but is not required to perform data extraction of all records in the nest.
a. Which data does Adaptive Smart Tags use? #
Recommendations are generated for abstracts or full-text PDFs at the user’s discretion. You instruct the model through:
- Tag Names
- Hierarchical structure of tags
- Question Types
- Question
- Contents (this includes text, table, options and numerical contents created alongside tags)
b. How does the model work? #
Adaptive Smart Tags uses an OpenAI LLM to identify relevant concepts or answer questions about plain-text reductions of abstracts and full-text PDFs. The model’s recommendations relate to the PDF as an annotation using fuzzy (edit distance) search.
The model, and OpenAI in general, is not trained or updated using your data.
Synthesis AI Disclosure #
The records included in Synthesis, as well as the Tags applied to underlying reports, may have been collected by users with assistance of Artificial Intelligence. The Artificial Intelligence tools are generally integrated with direct researcher oversight, and the nest owners have final responsibility for the accuracy of all Screening and Tagging.
Data Security & Protection using AI #
At Nested Knowledge, we understand the importance of safeguarding your data. We have robust security measures in place designed to keep your information private, secure, and accessible. Nested Knowledge internally defines and adheres to numerous security policies designed to maintain the security & privacy of user data while maintaining high uptime with strong disaster recovery measures.
In regard to our database, data is gated behind standard, best practices authentication and authorization measures, and each project is logically separated from other projects. All network communications, within our app and to the client, are encrypted. Our sub-processors (e.g. OpenAI) are held to a data processing agreement (DPA) and reviewed prior to addition to addition to our stack. We do not work with sub-processors who repurpose or resell your data.
Please contact us if you require further information.

