Nested Knowledge offers a variety of AI-enhanced tools that make the systematic review process smoother and easier for users. Below are our key AI features and the review stages in which they can be used:
1. Smart Search #
Smart Search is a tool that assists you in building a search query based on your research question. In particular, you can input and refine a research question in order to generate three PubMed queries of varying sizes for you to finalize and edit as an Automatic Search. When refining a research question, a chatbot will prompt you to answer questions on specifics such as demographics, outcomes to help build out a better research question.

After generation, three queries of varying sizes are displayed for you to Finalize.
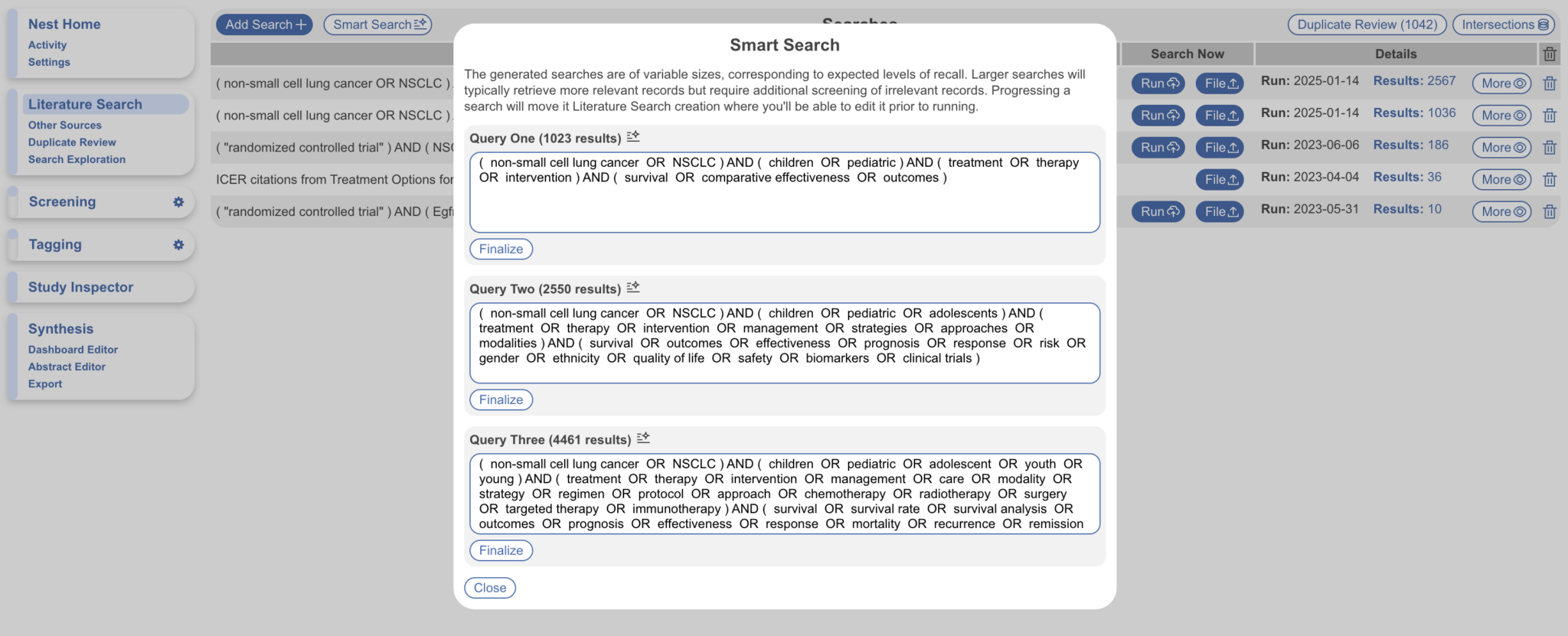
Upon finalizing, you may make edits, select a search engine and add a date filter as any normal Automatic Search.
2. RoboPICO #
Search Exploration #
RoboPICO works to provide the most commonly reported Population, Interventions, Comparators and Outcomes (PICOs; in red) in Search Exploration to help you build an effective search query. When you use the Search Exploration tool, RoboPICO automatically runs when you hit “Refresh Exploration.” You can select these terms, view their definitions, and build them into your search query (in orange).
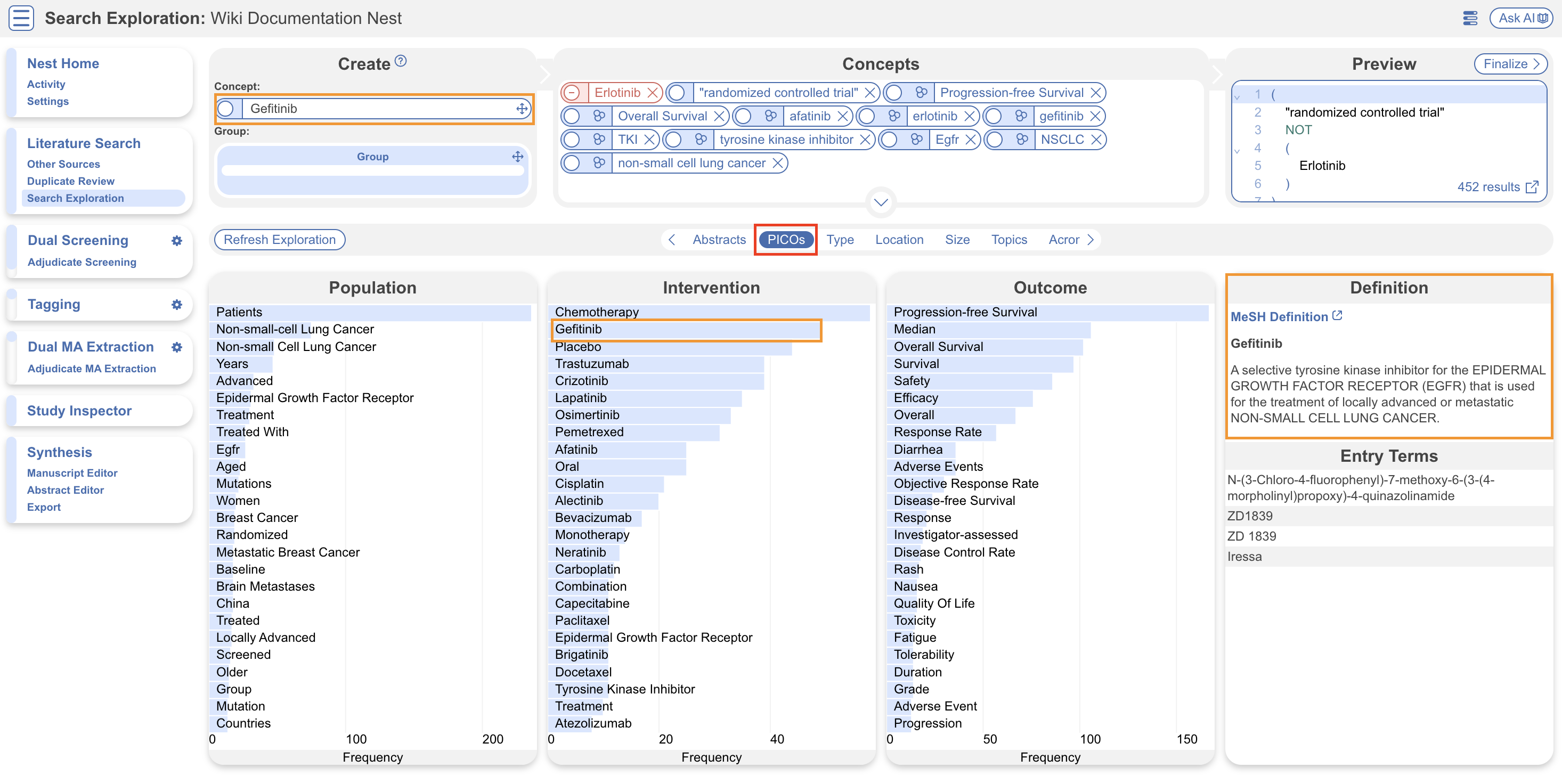
Screening #
RoboPICO also auto-highlights PICOs found in Abstracts during Screening to aid you to more efficiently make a decision on inclusion or exclusion of the record but may be toggled off (in red).

3. Bibliomine #
Literature Search #
The Nested Knowledge Bibliomine feature auto-extracts citations when you upload a pdf of any previous systematic review or landmark study and imports all cited references as records directly into your nest. This allows for fast updating of existing reviews and turns them into living reviews through quick implementation in the software. Alternatively, citation mining from an existing project pdf builds a solid foundation for a new project in your field of interest.
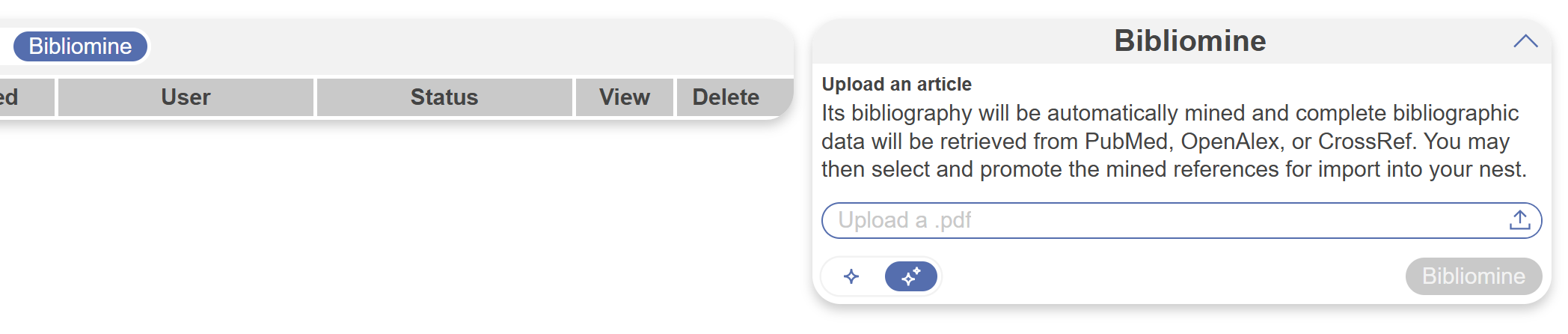
4. Robot Screener #
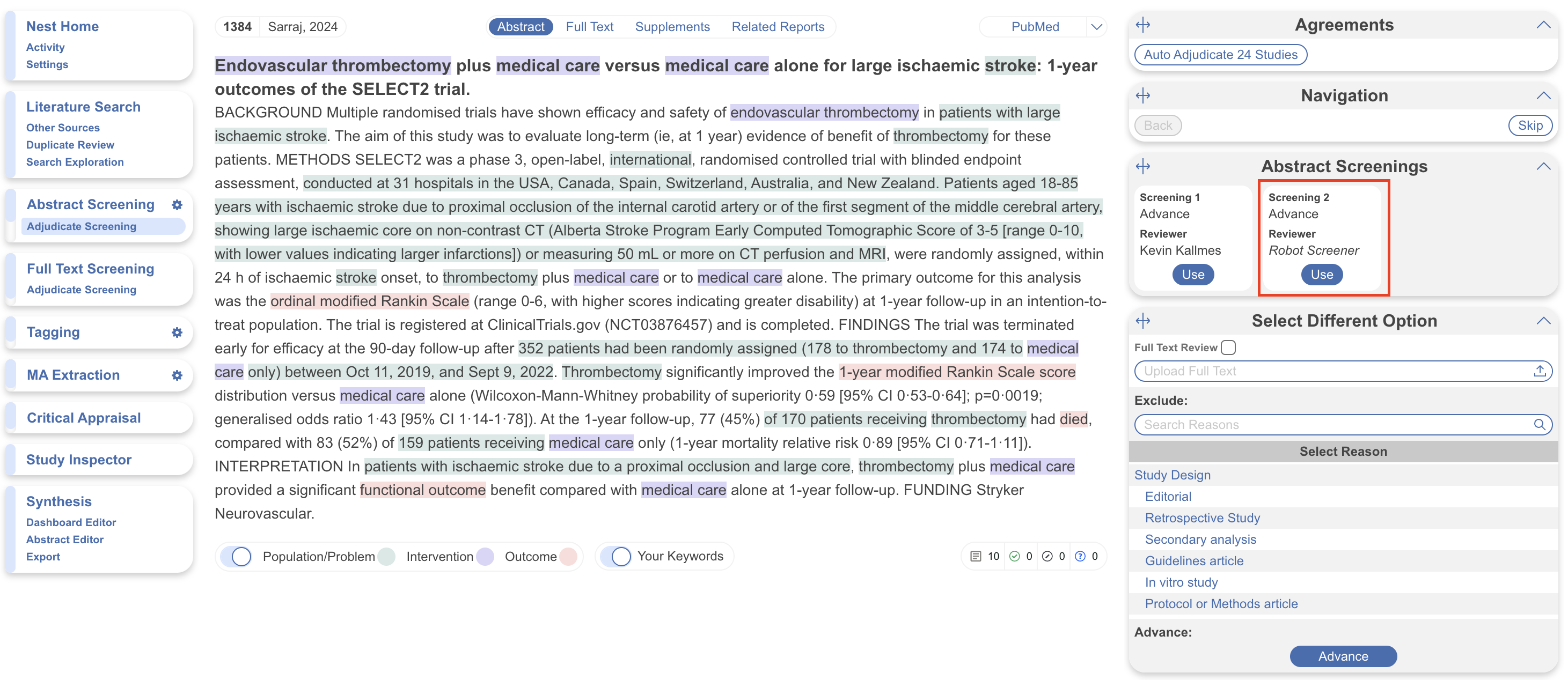
Dual Screening #
Robot Screener replaces one human reviewer with an AI reviewer in nests with a Dual Screening mode. It does require training (50 adjudicated screening decisions and 10 advancements or inclusions) prior to being switched on, but continually trains itself thereafter. Then, a human adjudicator reviews the preliminary screenings and makes the final decision.
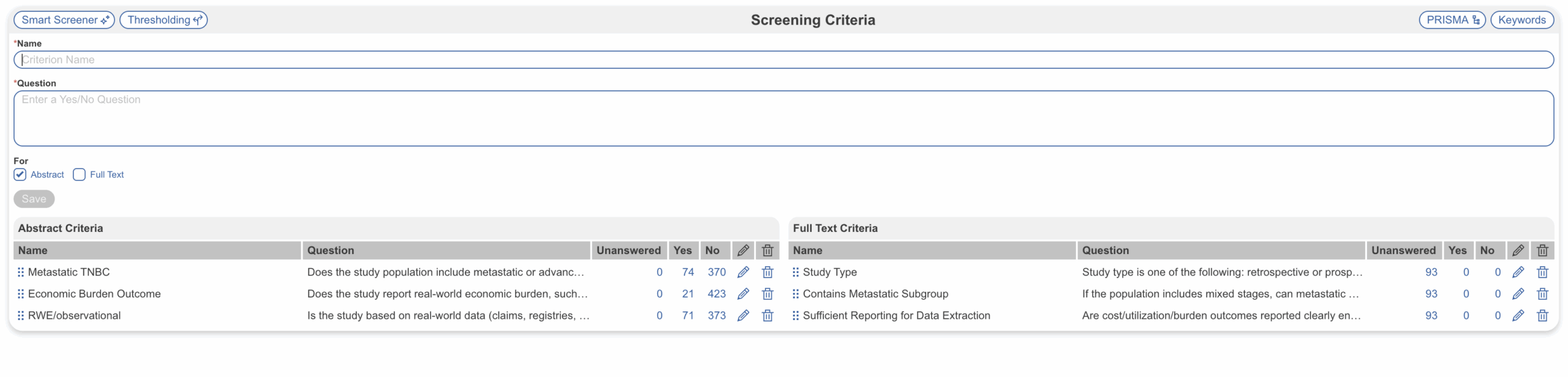
4. Criteria-Based Screening #
Criteria-Based Screening is a new workflow in Nested Knowledge that changes how you screen studies. Instead of simply marking studies as “Include” or “Exclude,” you answer a series of Yes/No questions based on your protocol’s inclusion criteria.
How it works:
Each screening question directly reflects one of your inclusion criteria. As you review a study, you answer each question, making your decision-making process more structured and transparent.
Two ways to use it:
- Manual screening – Answer the questions yourself for complete control over every decision
- AI-assisted screening – Use Smart Screener automation to have AI answer the questions, then review manually or set a threshold to assign screening decisions in bulk based on AI recommendations
What makes this unique:
This is the first feature in Nested Knowledge where AI can begin screening immediately without requiring any human-screened examples first. Simply define your criteria, and the AI can start working right away.
5. Adaptive Smart Tags #
Tagging/Data Extraction #
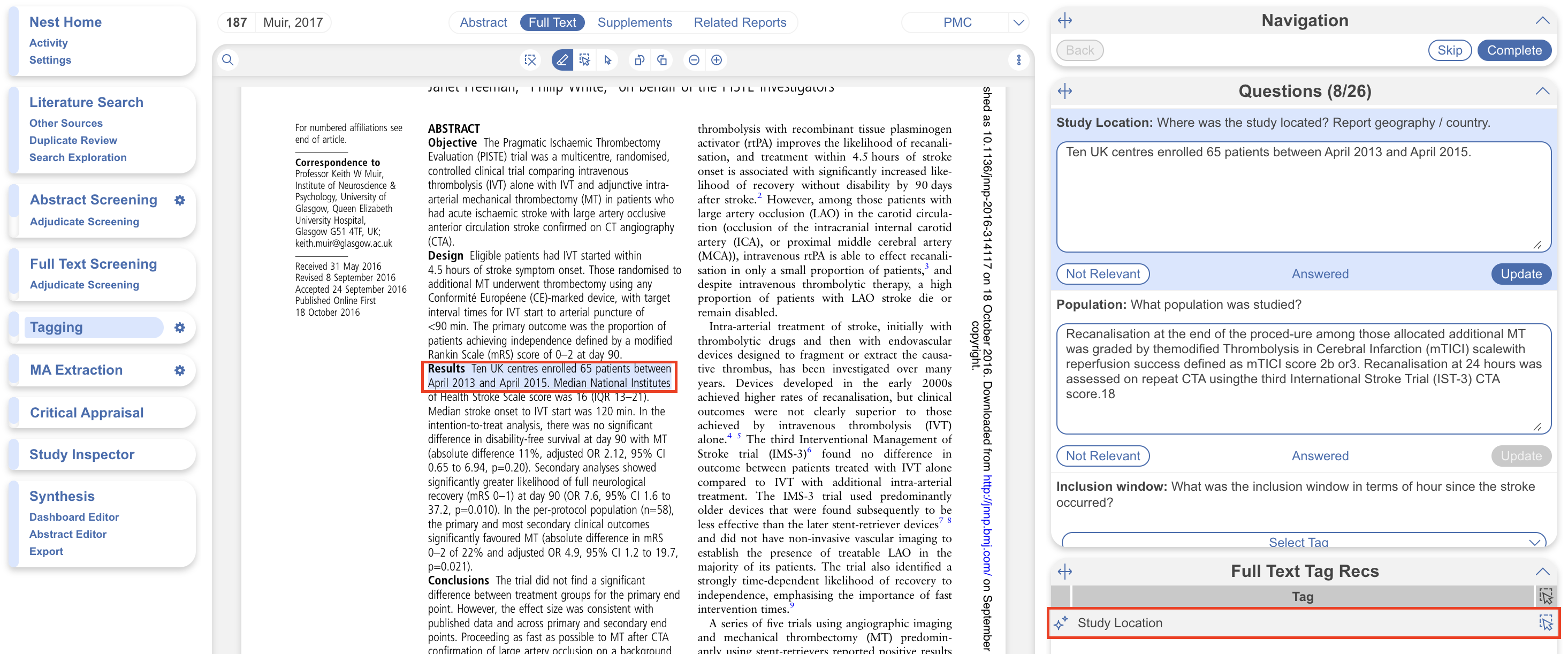
Adaptive Smart Tags (enterprise-level only) uses OpenAI’s LLM to search each included study with full text (default) for the most relevant evidence to extract alongside a tag. This is unlike Standard Tag Recommendations (available to all) which performs a simple keyword search (Standard Tag Recommendations). This feature helps to better answer questions (in Form-based modes) and saves time reading through pdfs to retrieve the data of interest.
Smart Tags may also be used for preliminary data extraction during Screening.
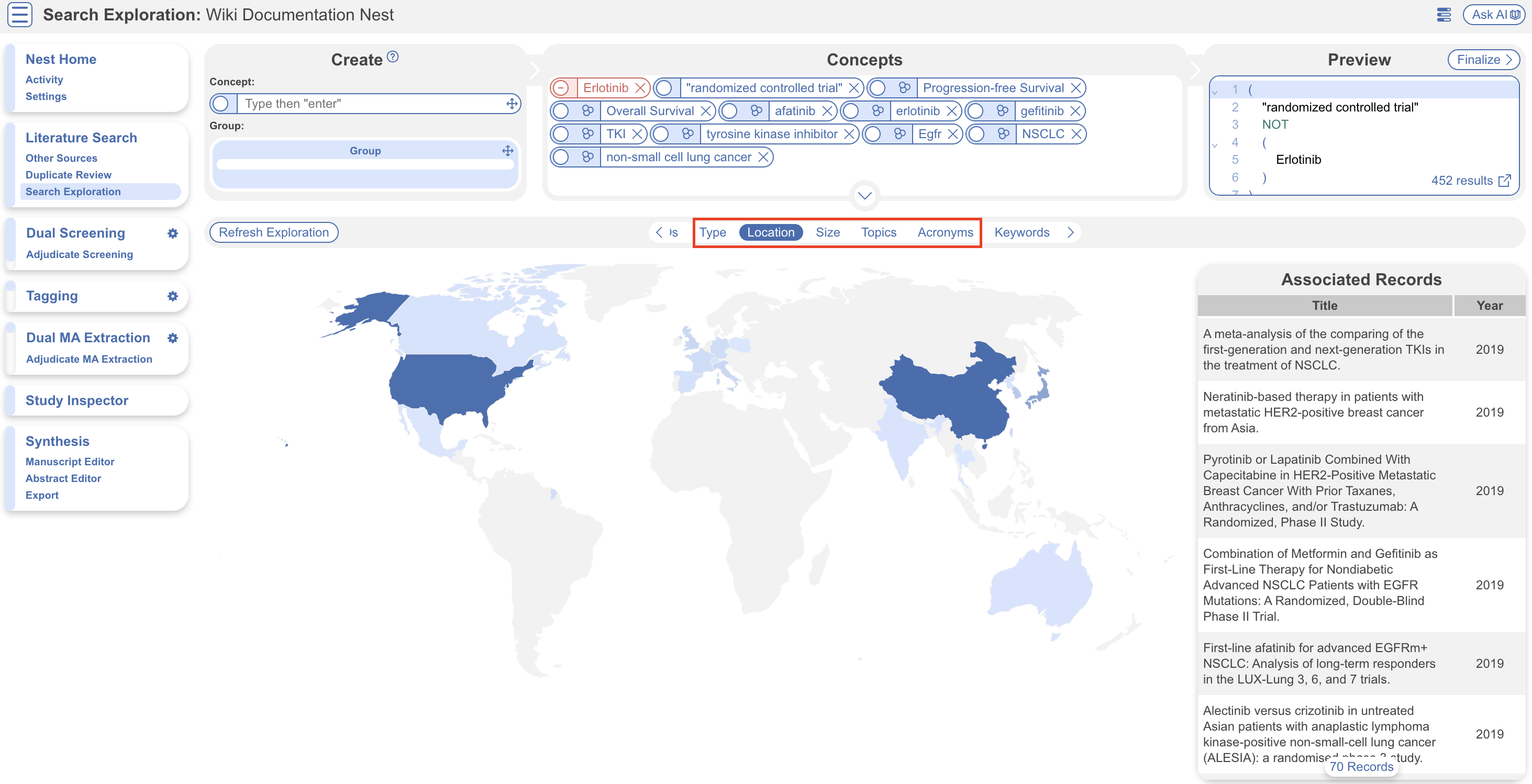
6. Core Smart Tags #
Search Exploration #
After inputting concepts of interest and refreshing exploration, Core Smart Tags identifies and displays Study Type via Sunburst diagram, Location via Choropleth map (below), Size via Histogram, and frequently reported Acronyms. Interact with each page and view associated records from a subset of 250 records from PubMed.
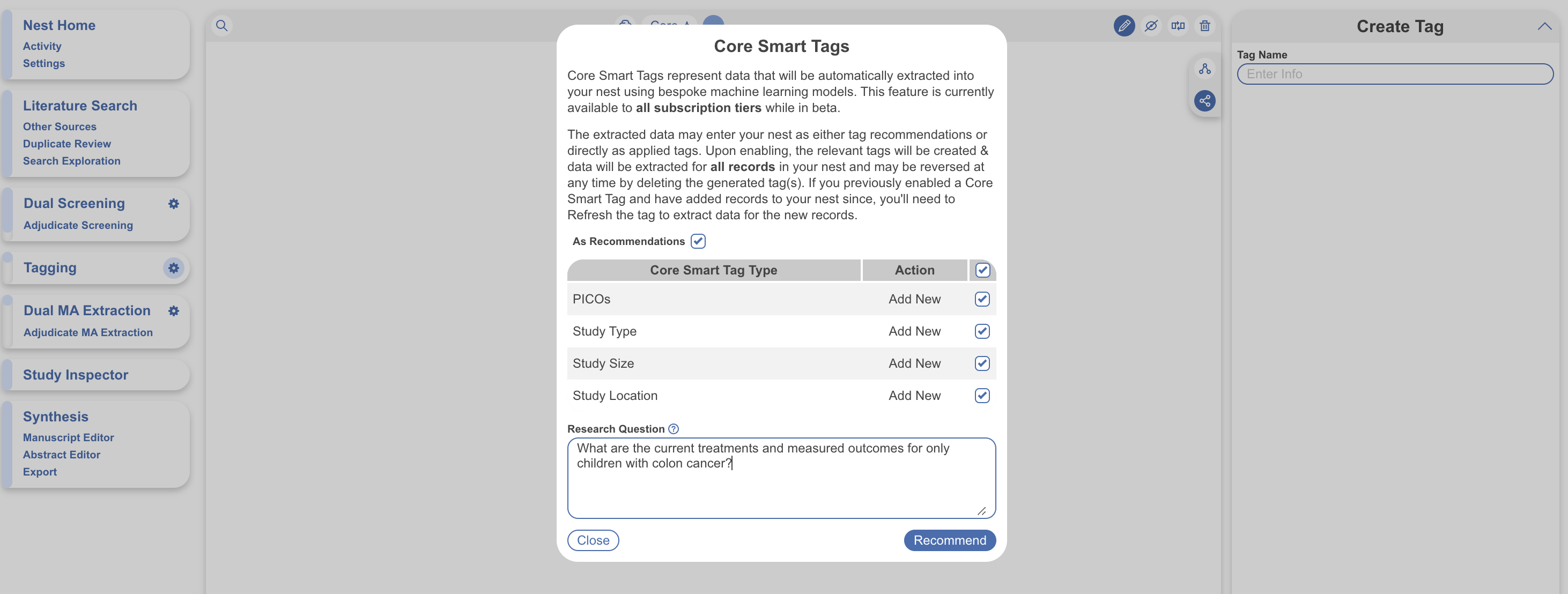
Tagging/Data Extraction #
After adding a search to your nest, you will want to configure a data extraction/tag hierarchy. Use Core Smart Tags to input your research question, generate a hierarchy of PICOs, Study Type, Location and Size and either recommend evidence or immediately extract this data from all studies in your nest.
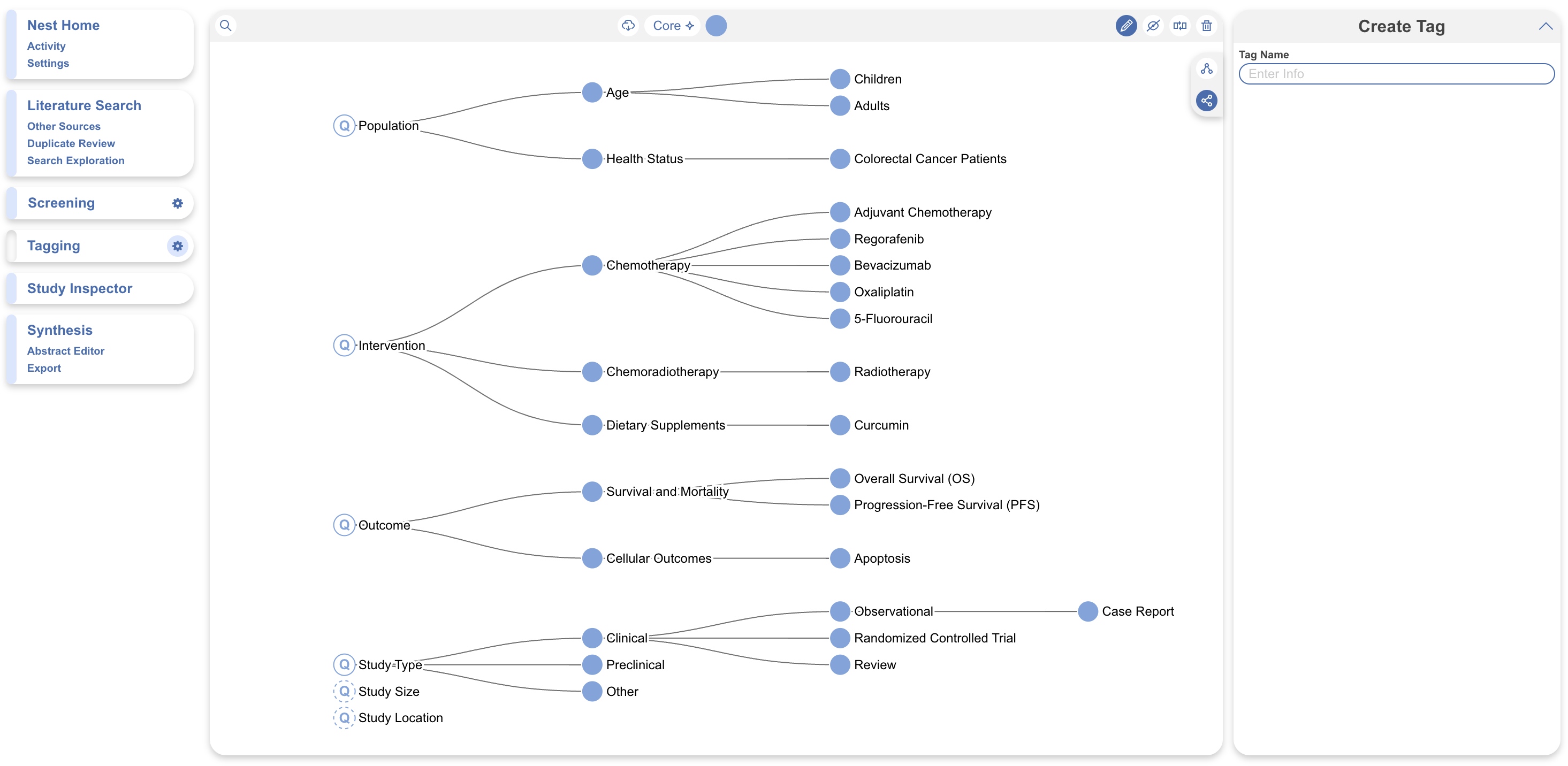
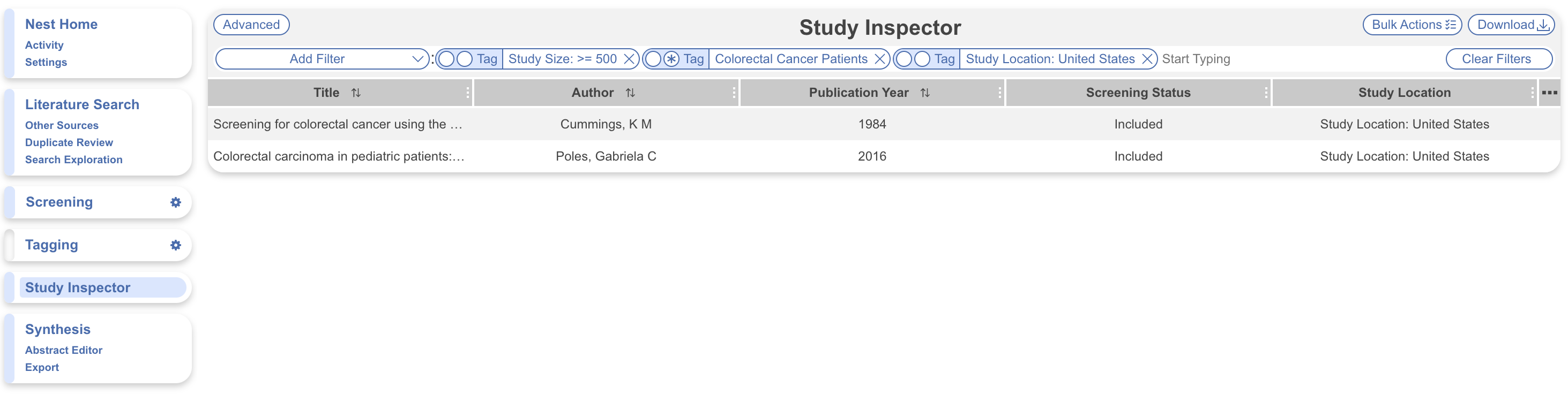
This not only produces a hierarchy for you, but you can then go on to immediately filter to subsets of studies to view and screen using Study Inspector:
Dashboard #
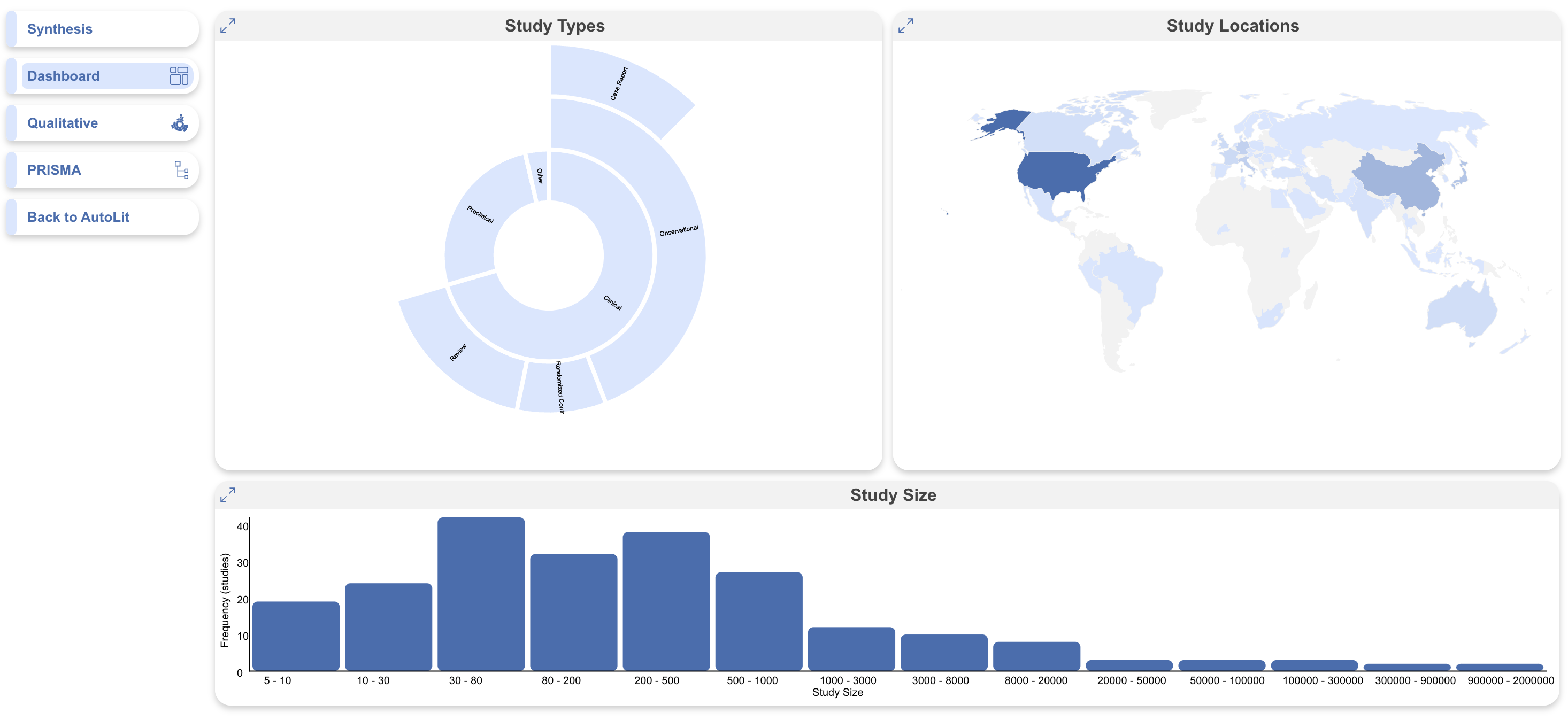
Core Smart Tags also allows you to display additional cards in Dashboard. This includes tags as Sunburst Cards, Study Location as a Map/Choropleth, and Study Types as a Histogram:
7. Smart Meta-Analytical Extraction #
After completing the tagging hierarchy within your project, you have the option to initiate Smart MA Extraction (SMAE) – a powerful feature designed to enable rapid-scope meta-analysis with minimal manual input. Leveraging Quantitative Synthesis, SMAE automatically extracts and harmonizes quantitative data from the tagged evidence.
Once Smart MA Extraction is complete, the extracted data will be available within the MA Extraction field. This view enables users to identify the interventions that were automatically extracted and included in the analysis. The extracted data elements are also accessible within the Quantitative Synthesis module.
Ask AI Support Chat Bot #
While not directly involved in the review workflow, our Ask AI Chat Bot is incredibly useful for any questions you might have on how to use the software and is accessible on any page in your nest in the top right.
Disclosure of AI Systems #
If you’d like to learn more about what powers each of these AI tools, feel free to check out our Disclosure of AI Systems in Nested Knowledge page.

