Background
In clinical research and strategic decision-making, speed and accuracy in synthesizing evidence are crucial. Traditional systematic literature reviews (SLRs) can take weeks or months, slowing insights into emerging therapeutic areas. To address this challenge, a global life sciences team commissioned Nested Knowledge to run an AI-assisted rapid review on a critical biomarker and therapeutic class intersection.
The focus was to evaluate whether the customer’s drug against comparators impacts inflammation, as measured by a key biomarker for measuring inflammation. While this biomarker is well-established as both a clinical and research endpoint, questions remain regarding the consistency, timing, and magnitude of treatment effects.
Methods
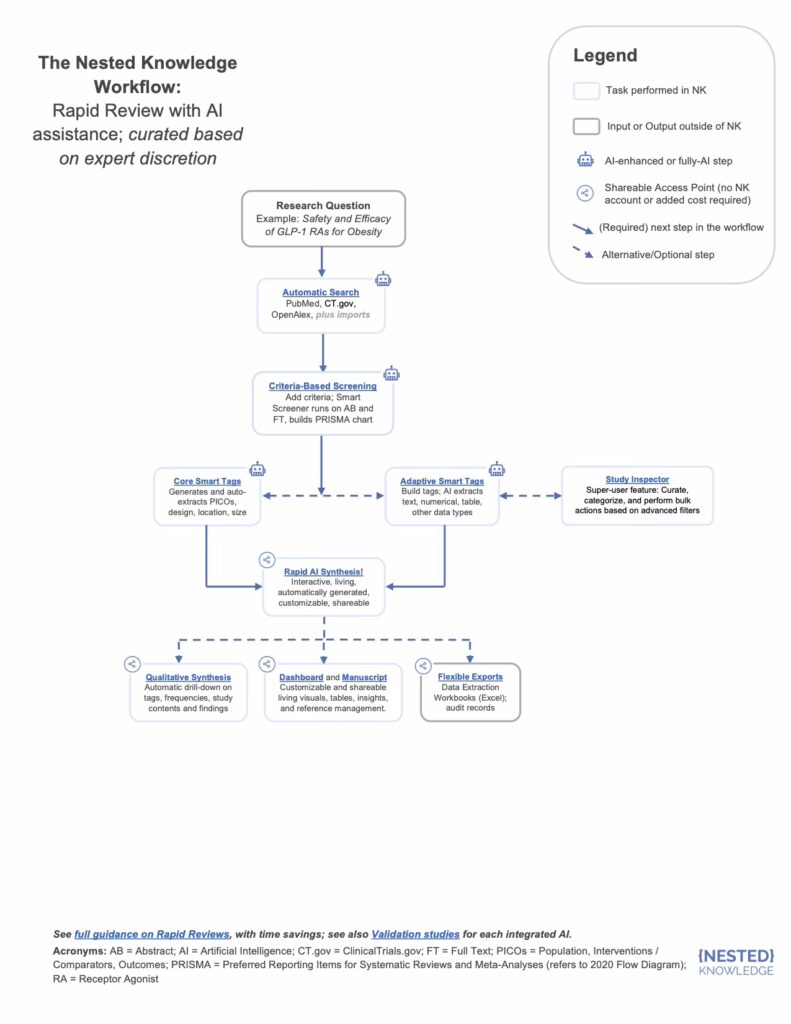
Nested Knowledge’s AI-enhanced platform was deployed to conduct the review. Key tools included:
- Smart Search: to identify and import all relevant published studies.
- Study Inspector: to configure screening criteria, confirm inclusion/exclusion, and bulk-screen results.
- Smart Tagging: AI-driven extraction of structured data elements (population, intervention, outcomes).
- Criteria-Based Screening: configured to ensure consistent inclusion based on key biomarker for measuring inflammation reporting.
A team of reviewers configured the AI, sanity-checked a subset of studies, and re-configured when needed through the process.
Review scope and outputs:
- Number of studies included: 54 abstract and 19 full-text trials and observational datasets.
- Data elements extracted: >120 (including sample size, intervention details, magnitude of key biomarker for measuring inflammation change, and time-to-reduction).
- Turnaround time: Initial review and synthesis delivered within 3 hours of the request.
Results
The AI-driven review synthesized outcomes across diverse clinical populations and study designs.
- Magnitude of Effect: Across the included studies, the therapeutic class was associated with consistent reductions in inflammation markers. Reported reductions in key biomarkers for measuring inflammation ranged from ~20% to >40% relative to baseline, with most studies showing statistically significant improvements.
- Consistency: The effect was observed regardless of study size (ranging from 10 to >1,900 patients), trial phase, or baseline inflammatory burden.
- Time to Reduction: Time to key biomarkers for measuring inflammation decrease varied across studies:
- Early signals were detectable as soon as 12–20 weeks in several trials.
- Sustained and more robust reductions were confirmed at 26–52 weeks in longer-term studies.
- Some exploratory studies showed trends toward reduction within 3 months, though not always statistically significant.
- Early signals were detectable as soon as 12–20 weeks in several trials.
Discussion
This case study demonstrates the ability of Nested Knowledge to rapidly synthesize nuanced biomarker data from across the clinical literature. Importantly:
- The review quantified both the magnitude and timing of therapeutic impact on the key biomarker for measuring inflammation.
- AI-assisted extraction ensured rapid turnaround, while human sanity-checks confirmed accuracy and contextual integrity.
- Even complex elements (time to outcome, subgroup patterns, varying formulations) were extracted and aggregated within hours.
Customer Outcome
Within 3 hours, the commissioning team received a structured, publication-quality synthesis of evidence on a strategically critical biomarker. This rapid insight enabled:
- Strategic positioning of the therapeutic class based on biomarker modulation.
- Data-driven communication with clinical and regulatory stakeholders.
- Acceleration of decision-making, without waiting weeks for a traditional SLR.
Conclusion
Nested Knowledge’s AI-enabled platform transformed a literature review task that would typically require weeks into a 3-hour, high-performance rapid review. By combining Smart Search, Criteria-Based Screening, and AI Tagging, the platform delivered clear evidence on the magnitude and timing of therapeutic impact on key biomarkers for measuring inflammation all while ensuring accuracy, reproducibility, and auditability.
